Upskill your team. Accelerate AI adoption.
Transform AI into your competitive advantage.
Trusted by teams at






The upskilling platform for AI and tech adoption
Get an expert assessment of your business goals and employee skillsets.


Last year we trained more data and AI apprentices than anyone else
1,500+
companies across the UK & US trust Multiverse
22,000+
learners across our AI, data and tech programmes
£2 billion
tracked return-on-investment for our customers to date
One platform for you and your team.
Business impact you can measure
Track quantifiable return on learning investment through business efficiencies, productivity and cost-savings.
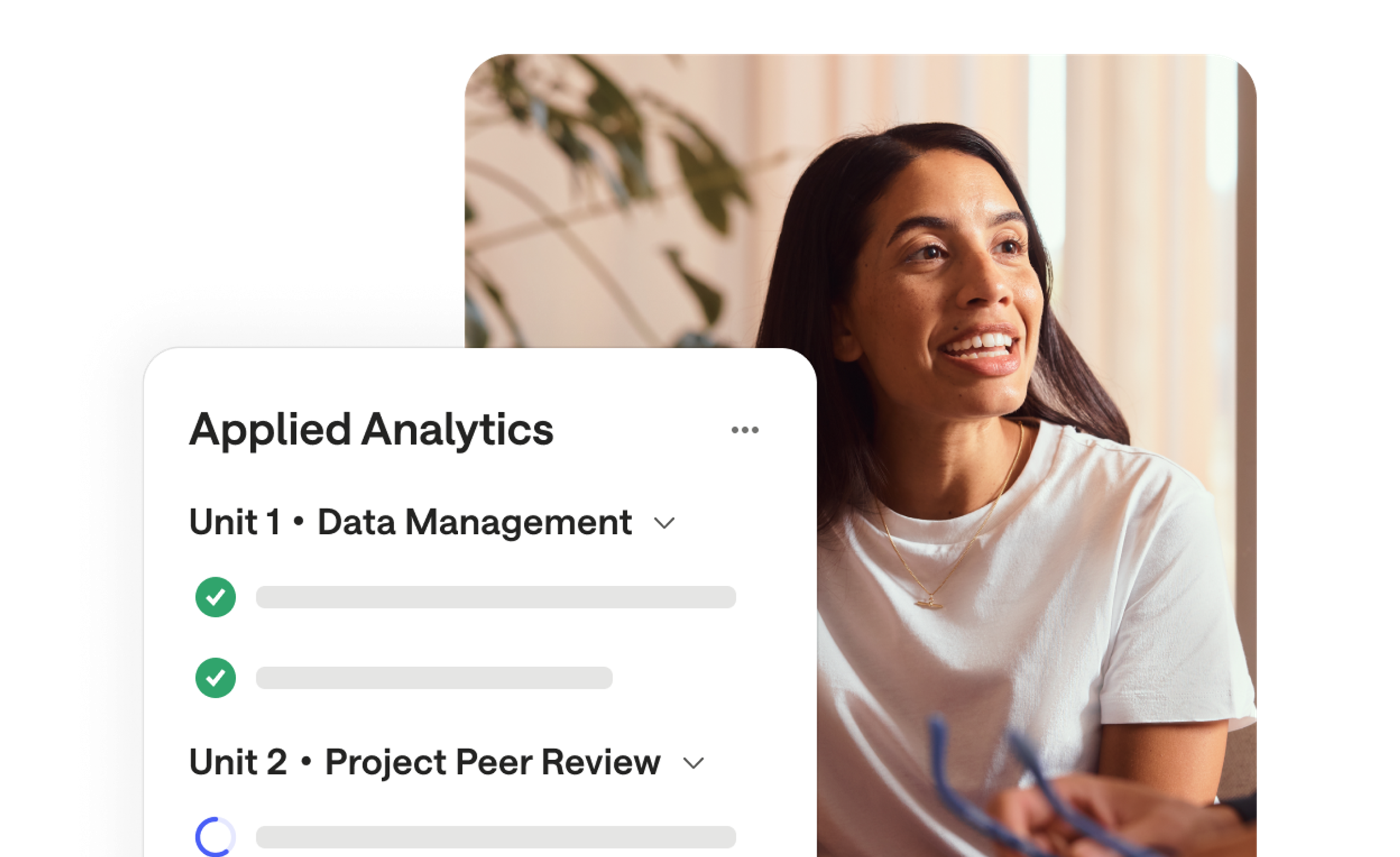
On-the-job learning
Apprentices learn in a real-world business setting, tailored to each individual and organisation.
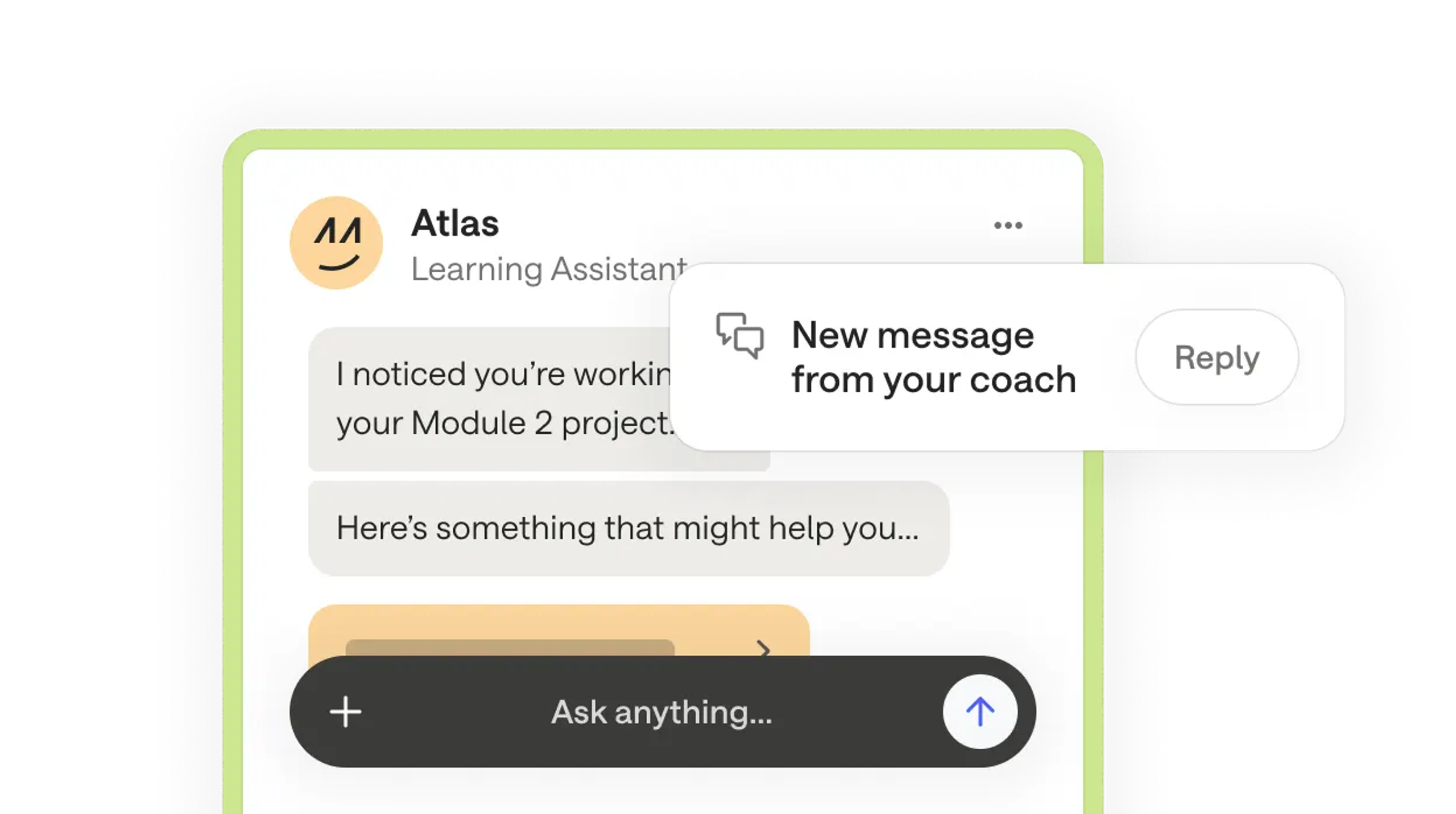
Expert-guided, AI-powered human coaching
An ecosystem of human and AI support means that learners are guided to success in their upskilling journey.
Transform careers
Everyone in your team has future-focused potential and deserves equitable access to economic opportunity.

Let’s get you to the right place
Popular programmes
Power upskilling and tool adoption at every level of your organisation.

Explore all programmes
Discover our full range to find the right fit for your goals.
How John Lewis Partnership stays one step ahead with data.
Discover how an iconic retailer transformed data capability and gave employees new confidence.

John Lewis Partnership03:21
Highlights
- Enabling efficiency with data
- Staying ahead of skills gaps
- Unlocking ROI from skills