With an apprenticeship, you can earn while you learn, get real-world experience and build a meaningful career in an industry you love. Knowing the different apprenticeship levels and options can help you choose which apprenticeship is right for you.
Different apprenticeship levels are available to suit your goals, whether you're entering the workforce, upskilling in your current role, or developing expertise in your field.
Making an informed choice about your future can set you on the right career path. To help you choose the best option for you, we'll guide you through the following:
- What is an apprenticeship?
- 4 types of apprenticeships
- Apprenticeship levels (Levels 2-7)
- Who can do an apprenticeship?
- Which apprenticeship is right for you?
- How to get an apprenticeship with Multiverse
What is an apprenticeship?
An apprenticeship is a nationally recognised qualification that allows you to earn a wage while you study. With an apprenticeship, you'll upskill, get hands-on industry experience and gain a relevant qualification as part of your paid job.
While completing your apprenticeship, you'll dedicate 80% of your working hours to on-the-job training and 20% to learning—your employer will pay you for both. You'll also receive employee benefits like paid holiday leave.
You can find relevant apprenticeships for most industries. However, the entry requirements and course structure will vary depending on the apprenticeship level and these factors:
- The profession you want to pursue or master
- How long you want to study
- Where you are in you’re career
4 types of apprenticeships
Whether you’re entering the workforce for the first time or you’re an existing employee hoping to upskill, there's an apprenticeship for you.
There are four different categories or types of apprenticeships in England:
- Intermediate (Level 2)
- Advanced (Level 3)
- Higher (Levels 4-7)
- Degree* (Levels 6 and 7)
Apprenticeship types are also sometimes called levels, because they each correspond to a numerical apprenticeship level (Levels 2-7).
Also, the exact apprenticeship terms may differ in other parts of the UK. In Scotland(opens new window), you'll find Foundation, Graduate, and Modern apprenticeships. Northern Ireland(opens new window) offers Level 2, Level 3 and Higher Level apprenticeships. Wales(opens new window) has similar apprenticeship types to England—the difference is Degree apprenticeships stop at Level 6.
*Degree apprenticeships are only available in England and Wales, but you can apply from across the UK.
Intermediate apprenticeships (Level 2)

Intermediate apprenticeships are a Level 2 qualification which is the equivalent of five GCSE passes. There are usually no qualification-specific entry criteria for Level 2 apprenticeships. However, employers might set job-specific entry requirements.
You'll also need to demonstrate to the education provider that you have what it takes to complete the course. You can show this through your enthusiasm for the subject or industry, relevant career goals or previous qualifications.
Level 2 apprenticeships are helpful if you need a 4 Standard Pass (previously grade C) or equivalent in English, Maths or both at GCSE. (You'll be able to gain Functional Skill equivalents as part of your apprenticeship, opening up more progression routes.)
They're also helpful if you've been out of the education system for a few years and want to build confidence before progressing.
Depending on your industry, job role and other factors, you can finish an Intermediate apprenticeship in 12 to 18 months.
Advanced apprenticeships (Level 3)

Advanced apprenticeships are equivalent to two passes at A Level and they’re classed as a Level 3 qualification.
You'll generally need a minimum of five passes at GCSE (including English and Maths) or a Level 2 apprenticeship qualification to be eligible. You can also use Functional Skill passes instead of English and Maths GCSEs.
If you live in England, you must stay in education until age 18(opens new window). Advanced apprenticeships are a good route for those who prefer a work-based alternative to Sixth Form or college.
Level 3 could be a natural continuation after completing a Level 2 apprenticeship. Progressing from Intermediate to Advanced can demonstrate your commitment to professional development and improve your potential career growth.
You can generally finish an Advanced apprenticeship in just over a year to two years. If you’re doing it part-time, it may stretch into three years, but it’s not the norm. For example, Multiverse’s Advanced apprenticeships for business and data literacy only take 13 months to complete.
Higher apprenticeships (Levels 4-7)

Higher apprenticeships cover Level 4, 5, 6 and 7 qualifications. You can achieve anything from a Foundation degree to a Master’s degree.
- Level 4 - Higher National Certificate (HNC), Level 4 NVQ, or the first year of an Undergraduate degree
- Level 5 - Higher National Diploma (HND) or Foundation degree
- Level 6 - Bachelor's degree
- Level 7 - Master's degree
You'll usually need five GCSE passes, including English and Maths or Functional Skill equivalents, to qualify for a Higher apprenticeship. Providers and employers may also consider your Level 3 qualifications (BTECs, Apprenticeships, A Levels or NVQs).
Employers sometimes set their own entry requirements specific to the Higher apprenticeship job role. They might ask for industry-relevant experience or qualifications. You don’t need industry experience to do any of our advanced apprenticeships.
Higher apprenticeships are work-related, vocational alternatives to theory-based study. They're ideal if you'd like a nationally recognised qualification, but becoming a full-time student or starting university doesn't appeal to you.
Higher apprenticeships can take anywhere from two to five years to complete.
Degree apprenticeships (Levels 6 and 7)

Degree apprenticeships cover Levels 6 and 7. Level 6 is equivalent to a Bachelor's degree, and Level 7 is equivalent to a Master's degree. Criteria for Degree apprenticeships vary, but as they're higher level qualifications, employers have specific requirements.
An employer might require you to have a Higher apprenticeship, five GCSE passes with English and Maths, or Level 3 qualifications. You might also need industry-relevant experience, including voluntary work.
When it comes to Multiverse degree apprenticeships, you’ll need the following minimum qualifications:
- A grade of 4/C GCSE (or equivalent) in Maths and English
- Be able to work in the UK
- Lived in the UK for at least three years
Currently, there are two Multiverse programmes—Technology Consulting and Advanced Data Fellowship—that offer a degree. It’s an Applied Degree, so you learn through personalised coaching and on-the-job experience rather than traditional classroom study.
Degree apprenticeships can offer a more affordable alternative to the full-time university route. You'll earn a wage while studying, and apprenticeships are employer-funded, so you avoid student debt.
They're also viable if you'd like a degree but would prefer to start your career and learn real-world skills immediately. Or you don't want to leave the workforce and would like to improve your career trajectory by upskilling.
Degree apprenticeships take anywhere from three to six years to complete.
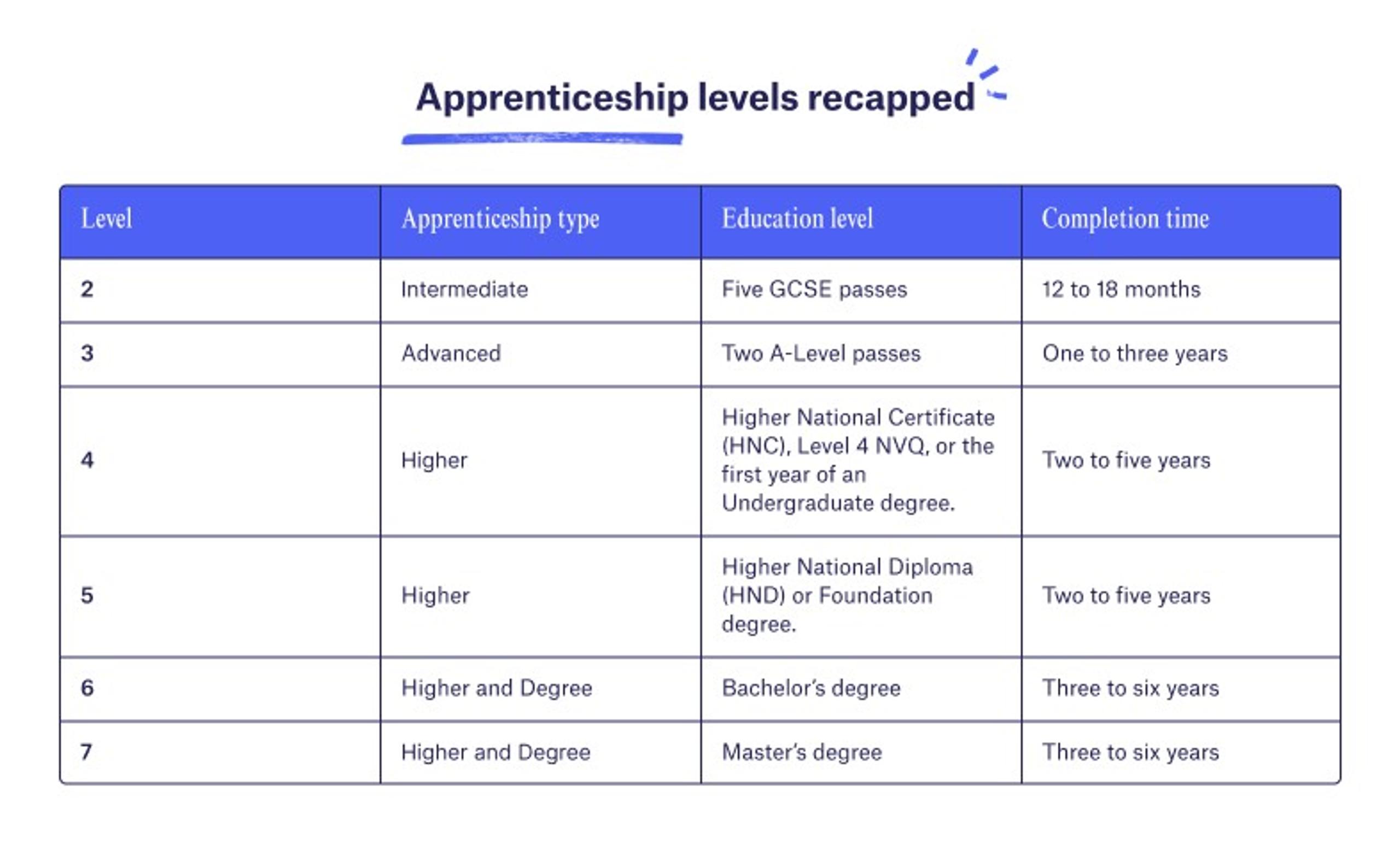
Apprenticeship levels
The six apprenticeship levels go from two to seven. Some apprenticeships combine several levels in one programme. For example, Multiverse’s Advance Data Fellowship covers Level 4, but you can complete a second part for Levels 5 and 6.
The higher the level, the more challenging the qualification. Across all levels, you'll earn a wage, enjoy employee benefits like holidays and get paid for time spent learning. To top it off, there's usually a permanent job waiting for you at the end of your apprenticeship.
Level 2
You can find Level 2 apprenticeships for most industries and job roles. Level 2 apprenticeships (Intermediate) are usually linked to entry-level roles, You don't usually need formal qualifications to be eligible as they're a lower level. However, having relevant industry experience or an interest in the sector helps.
If you don't have GCSE English and Maths (or equivalent), a Level 2 apprenticeship could be right for you. You'll be able to gain GCSE equivalents (without the intensity of a Level 3 or higher) as part of your apprenticeship.
Level 3
A Level 3 apprenticeship (Advanced) is the next step up. It’s usually a good fit for those starting out in their careers. You can find Level 3 apprenticeships for Data Technicians, Software Engineers, Veterinary Nurses, Personal Trainers and more.
If you passed GCSE English and Maths and show you're working at Level 2 or above, you can usually skip straight to Level 3. Many Level 2 and 3 apprenticeships require Functional Skills qualifications. These show that you have developed your knowledge of English and maths enough for the role. To gain the qualification, you study and take an assessment.
When relevant to the job role or industry, some Level 3 apprenticeships require you to complete Functional Skills in Information and Communication Technology (ICT). This can be helpful if you'd like to progress to Higher apprenticeships in digital and tech sectors.
Level 4
Level 4 (Higher) apprenticeships are helpful for those who've completed a Level 3 apprenticeship and are looking for a natural progression. You might also pursue a Level 4 apprenticeship if you fall into one of these categories:
- Career starter - someone who’s entered the workforce in the last few years and may be deciding what path they want to pursue (usually age 16-24)
- Builders - someone who wants to take the next step in their career, upskill, or future-proof their role
Remember, progression looks different for everyone. Level 4 apprenticeships can set you up for a new career or help you upskill and hone your expertise.
Level 5
Where Level 2 and even Level 3 apprenticeships can be broad, Level 5 apprenticeships tend to be more specialised. Level 5 apprenticeships are more challenging than lower levels as well, so employers will set more specific entry requirements. They’ll look for relevant qualifications and a problem-solving attitude to indicate applicants are committed to completing the course.
At Multiverse, we offer Level 4-6 apprenticeships to people who have recently done their A Levels. However, they need to prove their commitment to learning and becoming a master in their field. Industry experience isn’t a requirement, but it doesn’t hurt to have it.
Although you can start a Level 5 apprenticeship with Multiverse, most people that do them are further on in their career. They’ve typically worked in their field for eight to 15 years into and want to upskill or change careers.
For example, you might pursue a Level 5 apprenticeship if you’re in a data-heavy role (data science) and you need to upskill and learn how to code to automate. If you currently work in finance but want to become a Software Engineer, you could also do a Level 5 apprenticeship to transition.
Level 6
A Level 6 apprenticeship is equivalent to a full Bachelor's degree. There’s a broad range of Level 6 apprenticeships across industries. They're also more common for those that want to upskill, change careers, or further advance in their current field.
Level 6 apprenticeships are sometimes a progression from lower levels. If you start a Higher apprenticeship, you could progress to a Degree level. For example, an Advanced Data Fellowship programme takes you from Level 4 (Higher) to Level 6 (Degree).
Similar to a Level 5, you could do a Level 6 apprenticeship to upskill in your current role. If so, it could be worth raising this with your Line Manager in your next 1:1 meeting. Sometimes employers offer an educational stipend, fund Continuing Professional Development (CPD) or have an Apprenticeship Levy allowance(opens new window) available.
Level 7
There are Level 7 apprenticeships for Doctors, Game Programmers, Senior People Professionals, Creative Industries Production Managers and more.
Since Level 7 apprenticeships are the equivalent of a Master's degree, the entry requirements are strict. Expect training providers and employers to ask for more hours of relevant experience or an Undergraduate degree or equivalent.
Apprenticeship levels recapped
Who can do an apprenticeship?
You can do an apprenticeship in an existing or new role, provided the course is relevant to your job. Apprenticeship entry requirements vary depending on the level, industry, learning provider and employer. You can generally apply for an apprenticeship in England if you're:
- 16 or over
- Not in full-time education
- Currently living in England
- Have the right to work in England
The criteria may differ if you live in Scotland(opens new window), Wales(opens new window) and Northern Ireland(opens new window).
Apprenticeship providers have varying requirements. The requirements for Multiverse apprenticeships depend on the specific programme. At minimum, the requirements for eligibility are that you must:
- Be 16-24 years of age
- Have the right to work in the UK and lived there for the last three years
- Be able to provide GCSE English & Maths 4-9 (C-A*) or equivalent
- Not have completed a university degree
Which apprenticeship is right for you?
Choosing the right apprenticeship for you depends on a few factors—your interests, career goals, qualifications and experience.
Interests
If you prefer to start working over staying in full-time education, consider your interests first. Let's say you're fascinated by technology. You may have done well at GCSE ICT and started to learn to code in your spare time.
You're legally required to stay in education, but a hands-on approach suits your learning style. Plus, the end goal of completing a Computer Science degree at university doesn't appeal to you.
A tech apprenticeship programme could be a great way to develop your practical skills and kick-start your career in tech.
Career goals
Let's take this idea further, using the tech industry as an example. Say you're already working in a Junior Data Analyst role, but your ultimate career goal is to become a specialist in your field.
Completing an Advanced Data Fellowship programme (covering Levels 4-6) can give you the tools to become a trusted specialist.
Previous qualifications and experience
An apprenticeship provider should work with you to help you determine the best apprenticeship level for your needs. You can get a rough idea by looking at where you are in your career and where you want to go.
Anyone can do an apprenticeship, but are here are some examples to help you choose an apprenticeship level.
For those starting their careers, we usually recommend Level 3 apprenticeships. As mentioned, we have some career starters that do Level 4-6, but they provide additional proof of their qualifications or experience.
Those that have been working for years and want to upskill or change careers, consider Level 4-6 apprenticeships.
How to get an apprenticeship with Multiverse
As a Multiverse apprentice, you earn a competitive salary while you learn on the job. We provide business, digital and tech apprenticeship programmes that give hands-on practical learning experiences. Unlike university, our apprenticeships are fully funded and come at no expense to you.
The first step is to apply for a paid Multiverse apprenticeship. To be eligible, you must be at least 16 with the right to work in the UK. You'll also need at least a grade of 4/C GCSE (or equivalent) in Maths and English.
You'll then create a profile of your skills, traits, and experiences during the application process. Next, we'll get to know you and your goals for your future. Then, we'll help you land a paid apprenticeship at a top company.
Apply for an apprenticeship today(opens new window) and join the 93% of Multiverse apprentices who completed their programme and landed a job in their field within 90 days.







